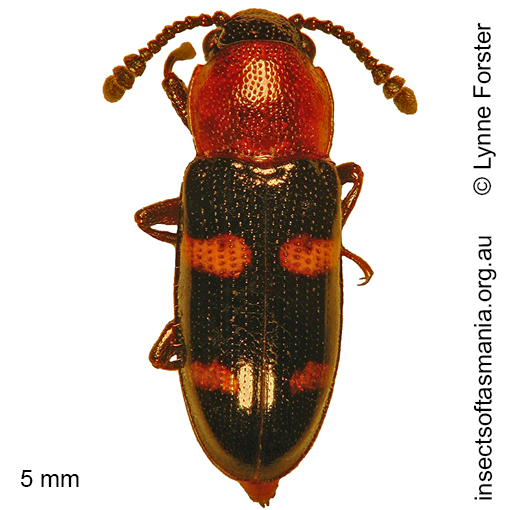
Thallis vinula Erichson, 1842 (a species of pleasing fungus-beetle)
Basis for Tasmanian occurrence
Semmens, T.D., McQuillan, P.B. & Hayhurst, G. (1992). Catalogue of the Insects of Tasmania. Government of Tasmania: Department of Primary Industry, 104 pp. (as Thallis vinula)
TMAG collections
Classification
Order: Coleoptera
Suborder: Polyphaga
Superfamily: Cucujoidea
Family: Erotylidae
Subfamily: Erotylinae
Tribe: Dacnini
Morphology
Typical length (mm): 5
Flightedness: winged and assumed capable of flight
Source literature on morphology and taxonomy (*primary taxonomic source, where identified):
*Erichson, W.F. (1842). Beitrag zur Insecten-Fauna von Vandiemensland, mit besonderer Beruecksichtung der geographischen Verbreitung der Insecten. Nicolai’schen Buchhandlung 8(1): 379 pages.
Ecology
Assumed larval feeding: fungus-feeder
Association with dead wood or old trees: at least facultatively saproxylic
Ecological attributes: — May occupy logs or trunks of Eucalyptus obliqua, at least temporarily, since found having emerged within six years of felling (Grove et al., 2009).
Collection method(s) for TMAG material: — Baited trapping (funnel trap) — Baited trapping (Ips pheromone) — Emergence trapping from cut billets of Eucalyptus obliqua (Harrison, 2007) — Emergence trapping from log of Eucalyptus obliqua — Flight intercept trapping (trough below Malaise trap) — Malaise trapping — Pipe trapping — Sticky trapping (substrate not specified) — Sticky trapping on Acacia dealbata — Sticky trapping on Eucalyptus globulus — Sticky trapping on Eucalyptus obliqua — Sticky trapping on Eucalyptus viminalis — Trapping using a range of devices placed in crown of Eucalyptus obliqua (Bar-Ness, 2005) — Vane trapping.
Source ecological literature:
Grove, S.J. (2009b). Beetles and fuelwood harvesting: a retrospective study from Tasmania’s southern forests. Tasforests 18: 77-99.
Bar-Ness, Y. (2005). Crown structure and the canopy arthropod biodiversity of 100 year old and old-growth Tasmanian Eucalyptus obliqua. Msc thesis, Univ. of Tasmania, Hobart.
Grove, S. et al. (2009). A long-term experimental study of saproxylic beetle … succession in Tasmanian Eucalyptus … logs… In: Fattorini, S. (Ed.), Insect Ecology and Conservation. Research Signpost, pp. 71-114.
Harrison, K.S. (2007). Saproxylic beetles associated with habitat features in Eucalyptus obliqua trees in the southern forests of Tasmania. PhD thesis, Dept. of Zoology, Univ. of Tasmania, Hobart.
Webb, G.A. & Simpson, J.A. (1991). Notes on some Australian fungus beetles and their hosts and parasites. Col. Bull. 45: 42-44.
Yee, M. (2005). The ecology and habitat requirements of saproxylic beetles native to Tasmanian wet eucalypt forests: potential impacts of commercial forestry practices. PhD thesis, Univ. of Tasmania, Hobart.