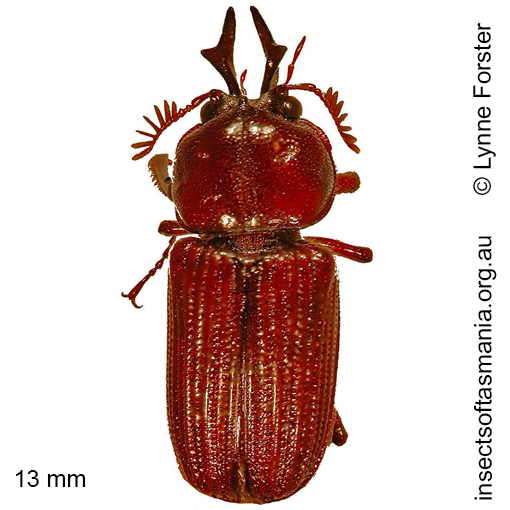
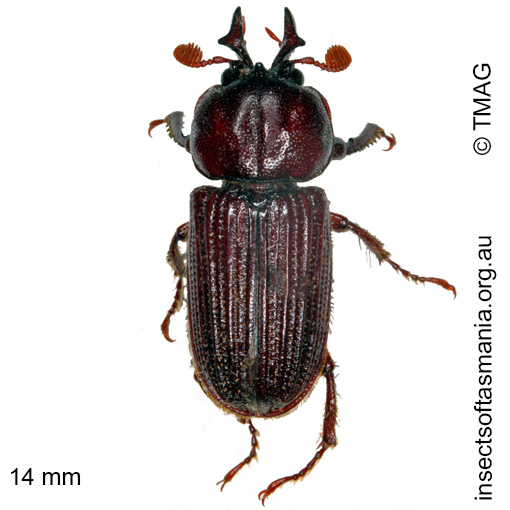
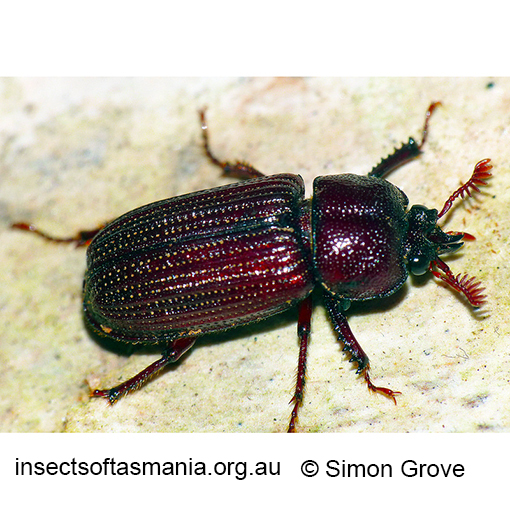
Syndesus cornutus (Fabricius, 1801) (a species of stag-beetle)
Basis for Tasmanian occurrence
Classification
Suborder: Polyphaga
Superfamily: Scarabaeoidea
Family: Lucanidae
Subfamily: Syndesinae
Morphology
Flightedness: winged and assumed capable of flight
Source literature on morphology and taxonomy (*primary taxonomic source, where identified):
*Fabricius, J.C. (1801). Systema Eleutheratorum secundum ordines, genera, species: adiectis synonymis, locis, observationibus, descriptionibus. 2. Bibl. Acad. Nov., Kill., 610 pages.
Ecology
Association with dead wood or old trees: obligately saproxylic
Ecological attributes: — Eucalyptus obliqua is a host-plant (Bashford, 1990a) — Eucalyptus sieberi is a host-plant (Bashford, 1990a) — Affiliated with older trees (Harrison, 2007) — Associated with brown spongy cubic rot Yee et al., 2006) — Associated with dry brown cubic rot (Harrison, 2007) — Associated with wet brown cubic rot (Harrison, 2007) — Found under large logs (Grove et al., 2006) — May occupy logs or trunks of Eucalyptus obliqua, at least temporarily, since found having emerged within a year of felling (Grove & Bashford, 2003) — May occupy logs or trunks of Eucalyptus obliqua, at least temporarily, since found having emerged within six years of felling (Grove et al., 2009).
Collection method(s) for TMAG material: — At light (with use of light-trap) — Baited trapping (funnel trap) — Emergence trapping from cut billets of Eucalyptus obliqua (Harrison, 2007) — Emergence trapping from log of Eucalyptus obliqua — Hand collection (substrate not specified) — Hand collection from under log of Eucalyptus sp. — Log-mounted flight intercept trapping — Panel trapping — Pipe trapping — Pitfall trapping — Vane trapping.
Source ecological literature:
Grove, S.J. & Bashford, R. (2003). Beetle assemblages from the Warra log decay project: insights from the first year of sampling. Tasforests 14: 117-129.
Grove, S.J. et al. (2006). What lives under large logs in Tasmanian eucalypt forest? Tas. Nat. 128: 86-93.
Yee, M. et al. (2001). Not just waste wood: decaying logs as key habitats …: the ecology of large and small logs compared. Tasforests 13: 119-128.
Bashford, R. (1990a). Tasmanian forest insects and their host plants: records from the Tasmanian Forestry Commission insect collection. Hobart: Tas. Forestry Commission, 32 pages.
Grove, S. et al. (2009). A long-term experimental study of saproxylic beetle … succession in Tasmanian Eucalyptus … logs… In: Fattorini, S. (Ed.), Insect Ecology and Conservation. Research Signpost, pp. 71-114.
Grove, S.J. & Yaxley, B. (2005). Wildlife habitat strips and native forest ground-active beetle assemblages in plantation nodes in northeast Tasmania. Aust. J. Entom. 44 (4): 331-343.
Harrison, K.S. (2007). Saproxylic beetles associated with habitat features in Eucalyptus obliqua trees in the southern forests of Tasmania. PhD thesis, Dept. of Zoology, Univ. of Tasmania, Hobart.
Yee, M. (2005). The ecology and habitat requirements of saproxylic beetles native to Tasmanian wet eucalypt forests: potential impacts of commercial forestry practices. PhD thesis, Univ. of Tasmania, Hobart.
Yee, M. et al. (2006). Brown rot in inner heartwood: why large logs support characteristic … beetle assemblages … In Grove, S.J. & Hanula, J.L. (eds.) Insect biodiv. and dead wood, pages 42-56. USDA For. Serv., SRS.