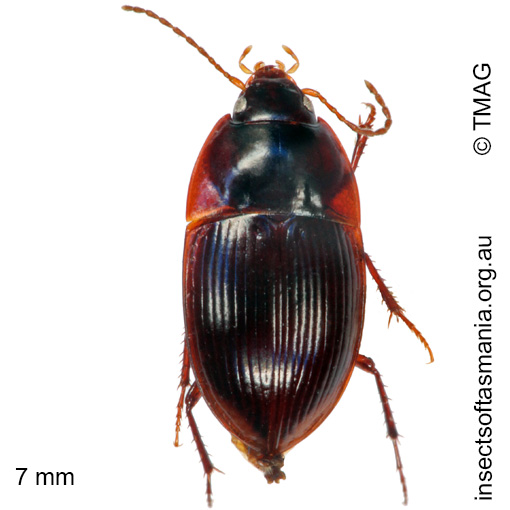
Stichonotus leai
Basis for Tasmanian occurrence
TMAG collections
Classification
Suborder: Adephaga
Superfamily: Caraboidea
Family: Carabidae
Subfamily: Migadopinae
Morphology
Flightedness: winged and assumed capable of flight
Source literature on morphology and taxonomy (*primary taxonomic source, where identified):
Sloane, T.G. (1920). The Carabidae of Tasmania. Proc. Linn. Soc. NSW 45: 113-178.
Ecology
Association with dead wood or old trees: at least facultatively saproxylic
Ecological attributes: — Affiliated with mature (unlogged) forest (Grove, 2009) — Affiliated with mature (unlogged) forest (Michaels, 1999) — Affiliated with open montane (>900 m altitude) environments (>900 m) (Forster & Grove, 2009) — Associated with fibrous surface rot (Yee et al., 2006) — May occupy logs or trunks of Eucalyptus obliqua, at least temporarily, since found having emerged within six years of felling (Grove et al., 2009).
Collection method(s) for TMAG material: — Emergence trapping from log of Eucalyptus obliqua — Hand collection (substrate not specified) — Pitfall trapping.
Source ecological literature:
Baker, S.C. (2000). Forest litter beetles and their habitat: a comparison of forest regenerated by wildfire and logging practices. Hons. thesis, Univ. of Tasmania, Hobart.
Baker, S.C. (2006b). Ecology and conservation of ground-dwelling beetles in managed wet eucalypt forest: edge and riparian effects. PhD thesis, Univ. of Tasmania, Hobart.
Grove, S. et al. (2009). A long-term experimental study of saproxylic beetle … succession in Tasmanian Eucalyptus … logs… In: Fattorini, S. (Ed.), Insect Ecology and Conservation. Research Signpost, pp. 71-114.
Grove, S.J. (2009c). Do wildlife habitat strips act as refuges for mature-forest carabid beetle assemblages? A case-study in Tasmanian wet eucalypt forest, Australia. For. Ecol. Manage. 259: 496-504.
Michaels, K.F. (1999a). Carabid beetles as biodiversity and ecological indicators. PhD thesis, Univ. of Tasmania, Hobart.
Yee, M. (2005). The ecology and habitat requirements of saproxylic beetles native to Tasmanian wet eucalypt forests: potential impacts of commercial forestry practices. PhD thesis, Univ. of Tasmania, Hobart.
Yee, M. et al. (2006). Brown rot in inner heartwood: why large logs support characteristic … beetle assemblages … In Grove, S.J. & Hanula, J.L. (eds.) Insect biodiv. and dead wood, pages 42-56. USDA For. Serv., SRS.