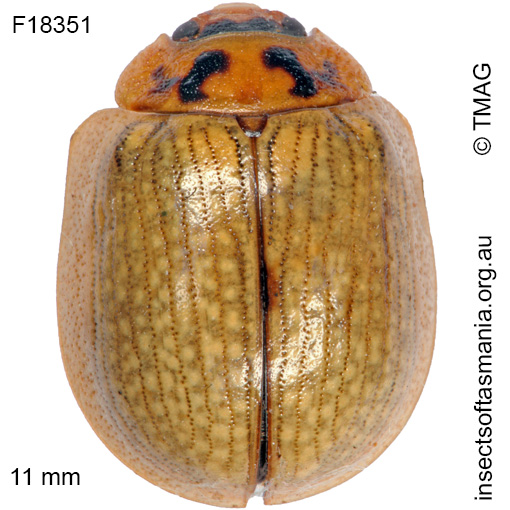
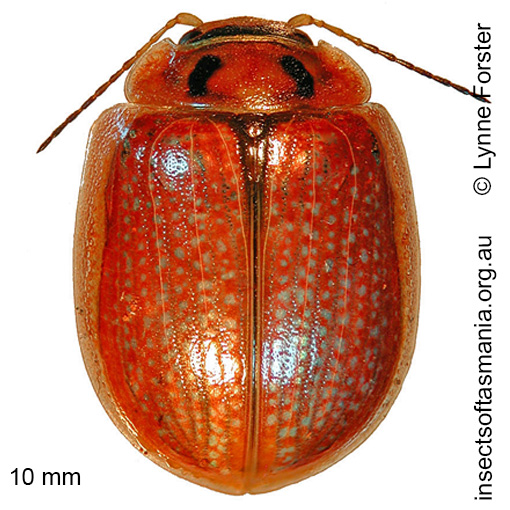
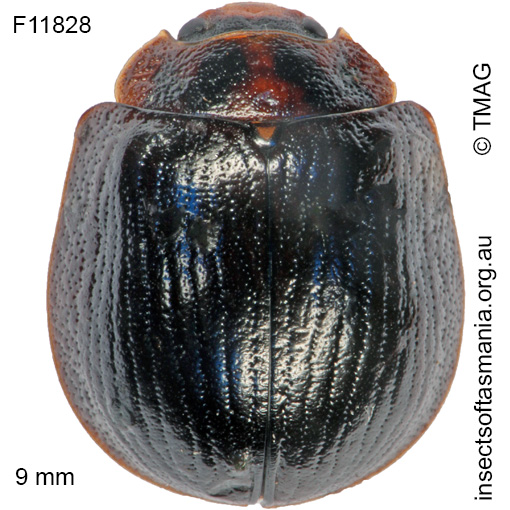
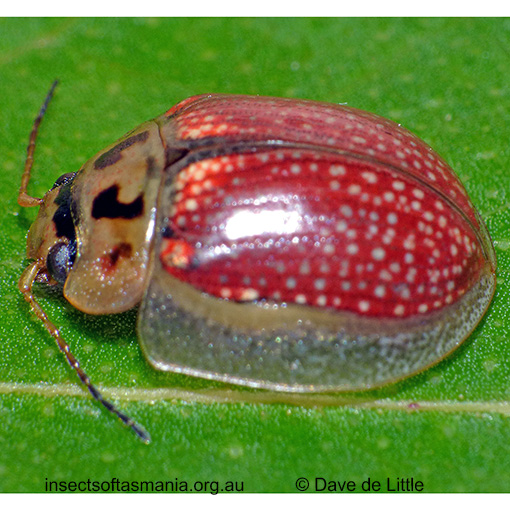
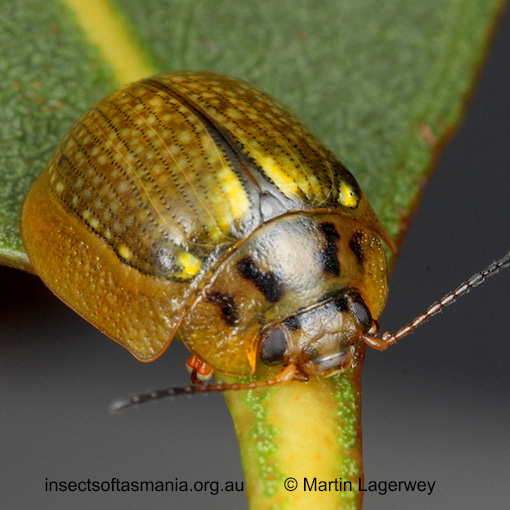
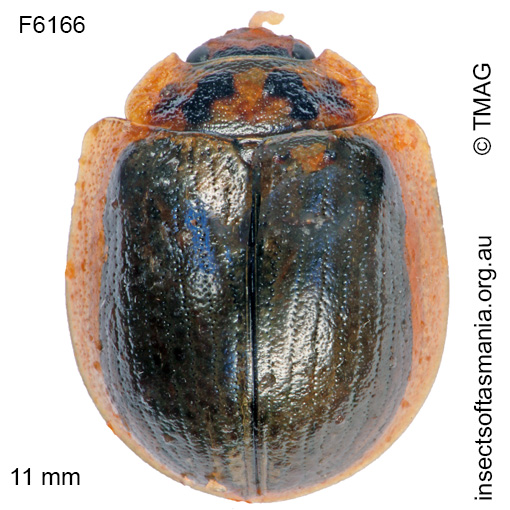
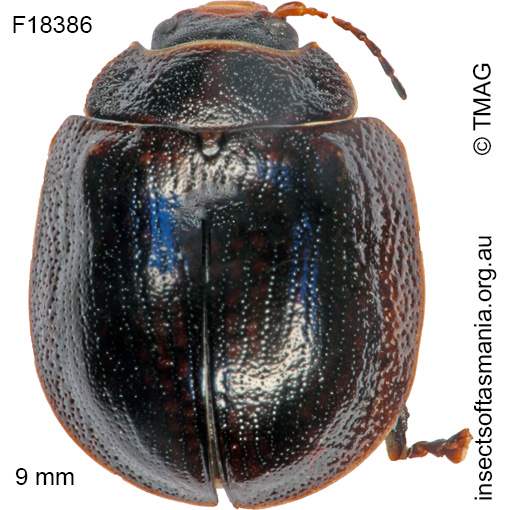
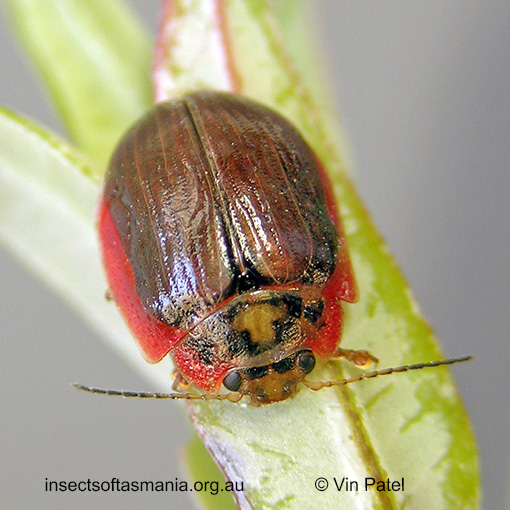
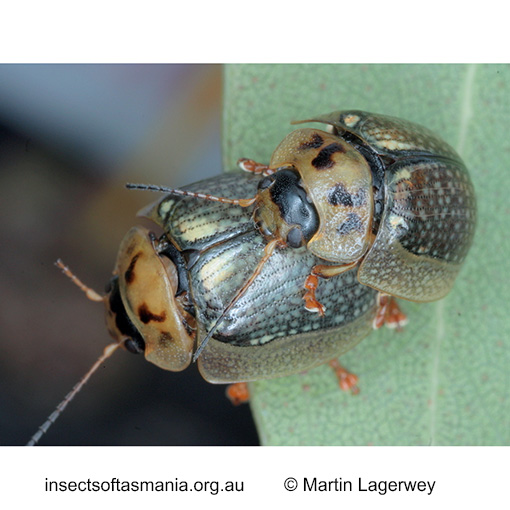
Paropsisterna agricola (a species of leaf-beetle)
Basis for Tasmanian occurrence
Semmens, T.D., McQuillan, P.B. & Hayhurst, G. (1992). Catalogue of the Insects of Tasmania. Government of Tasmania: Department of Primary Industry, 104 pp.
TMAG collecctions
Classification
Suborder: Polyphaga
Superfamily: Chrysomeloidea
Family: Chrysomelidae
Subfamily: Chrysomelinae
Morphology
Flightedness: winged and assumed capable of flight
Source literature on morphology and taxonomy (*primary taxonomic source, where identified):
deLittle, D.W. (1979). Taxonomic and ecological studies of the Tasmanian eucalyptus-defoliating paropsids …, with particular reference to Chrysophtharta bimaculata. … PhD thesis, Univ. of Tasmania, Hobart.
Ecology
Association with dead wood or old trees: not saproxylic
Ecological attributes: — Eucalyptus globulus is a host-plant (Bashford, 1990a) — Eucalyptus nitens is a host-plant (Bashford, 1990a) — Can inflict significant damage on Eucalyptus spp. (Elliott & deLittle, 1985).
Collection method(s) for TMAG material: — Hand collection (substrate not specified) — Hand collection from Acacia melanoxylon — Hand collection from Eucalyptus amygdalina/viminalis — Hand collection from Eucalyptus amygdalina — Hand collection from Eucalyptus delegatensis — Hand collection from Eucalyptus globulus — Hand collection from Eucalyptus nitens — Hand collection from Eucalyptus obliqua — Hand collection from Eucalyptus regnans/viminalis — Hand collection from Eucalyptus regnans — Hand collection from Eucalyptus tenuiramis — Hand collection from Eucalyptus viminalis — Malaise trapping — Not specified — Rearing in insectary from Eucalyptus nitens — Sticky trapping (substrate not specified) — Sticky trapping on Eucalyptus viminalis.
Source ecological literature:
Bashford, R. (1990a). Tasmanian forest insects and their host plants: records from the Tasmanian Forestry Commission insect collection. Hobart: Tas. Forestry Commission, 32 pages.
Beveridge, N. & Elek, J.A. (2001 ). Insect and host-tree species influence the effectiveness of a Bacillus thuringiensis …-based insecticide for controlling chrysomelid leaf beetles. Aust. J. Entom. 40: 386-390.
deLittle, DW. & Madden, J.L (1975). Host preference in the Tasmanian eucalypt defoliating Paropsini … with particular reference to Chrysophtharta bimaculata…and C. agricola … J. Aust. Entom. Soc. 14: 387-394.
Elliott, H.J. & deLittle, D.W. (1985). Insect pests of trees and timber in Tasmania. Hobart: Tas. Forestry Commission, 90 pages.
Kliejunas, J. T. & 9 others (2003). Pest risk assessment of the importation into the U.S. of unprocessed logs and chips of eighteen eucalypt species from Australia. Madison, WI: USDA Gen. Tech. Rep. FPL-137, 203 pages.
Lawrence, R. (1998 ). Responses of dependent communities to ontogenetic and genetic variation …: the case of the E… globulus x nitens hybrid system. Thesis, Univ. of Tasmania, 127 pages.
Lawrence, R. et al. (2003). Relative importance of plant ontogeny, host genetic variation, and leaf age for a common herbivore. Ecology 84: 1171-1178.
Nahrung, H. & Allen, G.R. (2003 b). Intra-plant host selection, oviposition preferences and larval survival of Chrysophtharta agricola … between foliage types of a heterophyllous host. Agric. For. Entom. 5: 155-162
Nahrung, H. & Allen, G.R. (2003a). Geographical variation, population structure and gene flow between populations of Chrysophtharta agricola …, a pest of Australian eucalypt plantations. Bull. Entom. Res. 93: 137-144.
Nahrung, H. & Allen, G.R. (2004a). Overwintering ecology of Chrysophtharta agricola: mechanism of reproductive diapause induction and termination. Aust. J. Zool. 52: 505-520.
Nahrung, H. & Allen, G.R. (2004b). Population dynamics of the chrysomelid leaf beetle Chrysophtharta agricola (Chapuis), a pest of Eucalyptus nitens plantations in Tasmania. Tasforests 15: 67-84.
Nahrung, H. & Allen, G.R. (2004c). Sexual selection under scramble competition: mate location and mate choice in the eucalypt leaf beetle Chrysophtharta agricola (Chapuis) in the field. J. Ins. Behav. 17: 353-366.
Nahrung, H. & Allen, G.R. (2005). Maintenance of colour polymorphism in the leaf beetle Chrysophtharta agricola (Chapuis) (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae: Paropsini). J. Nat. Hist. 39: 79-90.
Nahrung, H. & Reid, C. (2002). Reproductive development of the Tasmanian eucalypt-defoliating beetles Chrysophtharta agricola (Chapuis) and C.bimaculata (Olivier) … Col. Bull. 56: 84-95.
Nahrung, H. (2003). Reproductive ecology of Chrysophtharta agricola (Chapuis) (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae). Hobart, doctoral thesis, School of Agric. Sci., Univ. of Tasmania, 348 pages.
Nahrung, H. (2004). Biology of Chrysophtharta agricola (Coleroptera: Chrysomelidae), a pest of Eucalyptus plantations in south-eastern Australia. Aust. For. 67: 59-66.
Nahrung, H. et al. (2001 ). Larval gregariousness and neonate establishment of the eucalypt-feeding beetle Chrysophtharta agricola (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae: Paropsini). Oikos 94: 358-364.
Nahrung, H. et al. (2004). Day-degree development and phenology modelling of the immature stages of Chrysophtharta agricola …, a pest of eucalpt plantations. Aust. J. Entom. 43: 177-183.
Nahrung, H.F. & Murphy, B.D., (2002). Differences in egg parasitism of Chrysophtharta agricola … by Ennogera nassaui … in relation to host and parasitoid origin. Aust. J. Entom. 41: 267-271.
Nahrung, H.F. (2002). Biological differences between mainland and Tasmanian Chrysophtharta agricola, a Eucalyptus leaf beetle . Tas. Nat. 124: 56-64.
Ramsden, N. & Elek, J.A. (1998). Life-cycle and development rates of the leaf-beetle Chrysophtharta agricola … on Eucalyptus nitens at two temperature regimes. Aust. J. Entom. 37: 238-242.
Rapley, L.P. et al. (2004). Genetic variation in Eucalyptus globulus in relation to susceptibility from attack by the southern Eucalyptus leaf beetle, Chrysophtharta agricola. Aust. J. Bot. 52: 747-756.
Rice, D.R. (2005). The larval parasitoid guild of Chrysophtharta agricola …: host – parasitoid ecological and developmental interactions. Doctoral thesis, School of Agric. Sci., Univ. of Tasmania, 228 pages.
Seeman, O. & Nahrung, H. (2004). Female biased parasitism and the importance of host generation overlap in a sexually transmitted parasite of beetles. J. Parasit. 90: 114-118.
Taylor, R.J. (1990). Occurrence of log-dwelling invertebrates in regeneration and oldgrowth wet sclerophyll forest in southern Tasmania. Pap. Proc. Roy. Soc. Tas. 124: 27-34.