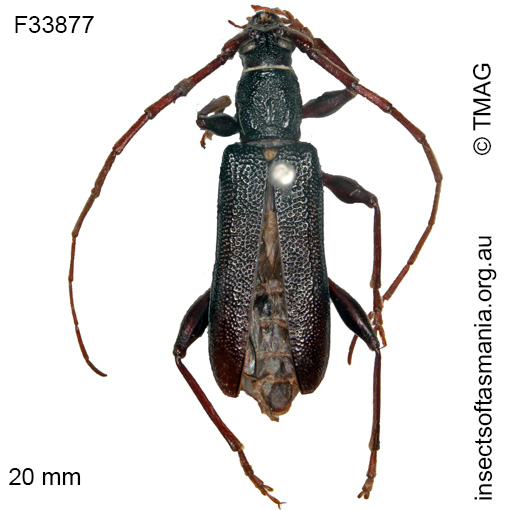
Callidiopis scutellaris
Basis for Tasmanian occurrence
TMAG collections
Classification
Suborder: Polyphaga
Superfamily: Chrysomeloidea
Family: Cerambycidae
Subfamily: Cerambycinae
Tribe: Callidiopini
Morphology
Flightedness: winged and assumed capable of flight
Source literature on morphology and taxonomy (*primary taxonomic source, where identified):
*Fabricius, J.C. (1801). Systema Eleutheratorum secundum ordines, genera, species: adiectis synonymis, locis, observationibus, descriptionibus. 2. Bibl. Acad. Nov., Kill., 610 pages.
Ślipiński, A. & Escalona, H. (2016). Australian longhorn beetles (Coleoptea: Cerambycidae), Volume 2: Subfamily Cerambycinae. CSIRO publishing, 640 pp.
Ecology
Association with dead wood or old trees: obligately saproxylic
Ecological attributes: — May occupy logs or trunks of Eucalyptus obliqua, at least temporarily, since found having emerged within a year of felling (Grove & Bashford, 2003) — May occupy logs or trunks of Eucalyptus obliqua, at least temporarily, since found having emerged within six years of felling (Grove et al., 2009).
Collection method(s) for TMAG material: — At light (with use of light-trap) — Baited trapping (funnel trap) — Emergence trapping from cut billets of Eucalyptus obliqua (Harrison, 2007) — Emergence trapping from log of Eucalyptus obliqua — Hand collection (substrate not specified) — Hand collection from within building — Malaise trapping — Not specified — Panel trapping — Rearing in insectary (host not documented) — Rearing in insectary from Eucalyptus amygdalina — Rearing in insectary from Eucalyptus delegatensis — Rearing in insectary from Eucalyptus obliqua — Rearing in insectary from Eucalyptus sieberi — Rearing in insectary from Eucalyptus tenuiramis — Sticky trapping (substrate not specified) — Sticky trapping on Eucalyptus viminalis — Sticky trapping on fire-scorched pine — Vane trapping.
Source ecological literature:
Grove, S.J. & Bashford, R. (2003). Beetle assemblages from the Warra log decay project: insights from the first year of sampling. Tasforests 14: 117-129.
Grove, S. et al. (2009). A long-term experimental study of saproxylic beetle … succession in Tasmanian Eucalyptus … logs… In: Fattorini, S. (Ed.), Insect Ecology and Conservation. Research Signpost, pp. 71-114.
Harrison, K.S. (2007). Saproxylic beetles associated with habitat features in Eucalyptus obliqua trees in the southern forests of Tasmania. PhD thesis, Dept. of Zoology, Univ. of Tasmania, Hobart.