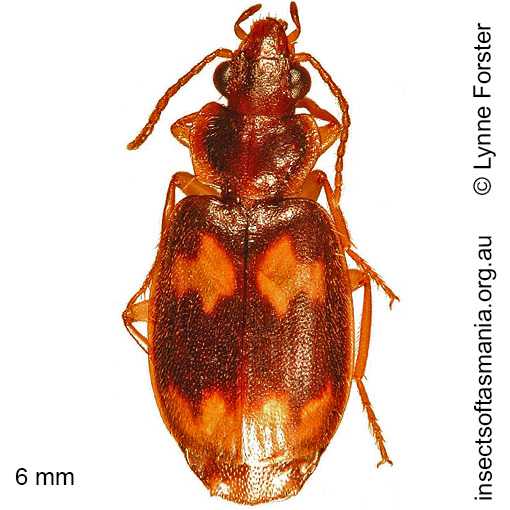
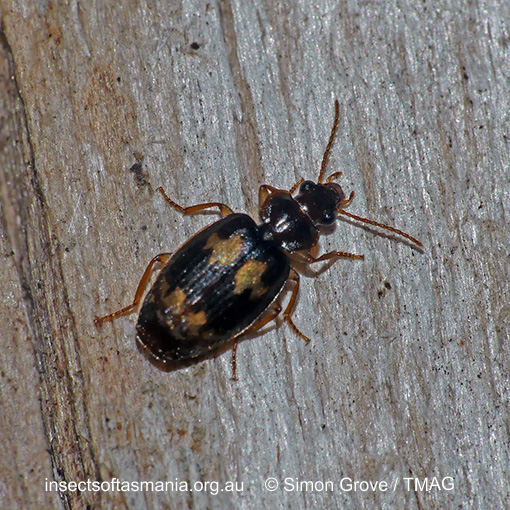
Agonocheila curtula (a species of ground-beetle)
Basis for Tasmanian occurrence
TMAG collections
Classification
Suborder: Adephaga
Superfamily: Caraboidea
Family: Carabidae
Subfamily: Harpalinae
Tribe: Lebiini
Morphology
Flightedness: winged and assumed capable of flight
Source literature on morphology and taxonomy (*primary taxonomic source, where identified):
*Erichson, W.F. (1842). Beitrag zur Insecten-Fauna von Vandiemensland, mit besonderer Beruecksichtung der geographischen Verbreitung der Insecten. Nicolai’schen Buchhandlung 8(1): 379 pages.
Sloane, T.G. (1920). The Carabidae of Tasmania. Proc. Linn. Soc. NSW 45: 113-178.
Ecology
Association with dead wood or old trees: at least facultatively saproxylic
Ecological attributes: — Dry sclerophyll forest can be suitable habitat (Michaels, 1999b) — May occupy logs or trunks of Eucalyptus obliqua, at least temporarily, since found having emerged within six years of felling (Grove et al., 2009).
Collection method(s) for TFIC material: — Baited trapping (funnel trap) — Baited trapping (Ips pheromone) — Emergence trapping from cut billets of Eucalyptus obliqua (Harrison, 2007) — Emergence trapping from log of Eucalyptus obliqua — Flight intercept trapping (trough below Malaise trap) — Hand collection (substrate not specified) — Hand collection from under bark (tree species not specified) — Knockdown fogging of canopy of Eucalyptus obliqua — Knockdown fogging of canopy of Nothofagus cunninghamii — Knockdown spraying of bark of Eucalyptus obliqua — Knockdown spraying of bark of Eucalyptus sp. — Pipe trapping — Pitfall trapping — Sticky trapping (substrate not specified) — Sticky trapping on Eucalyptus camaldulensis — Sticky trapping on Eucalyptus globulus — Sticky trapping on Eucalyptus obliqua.
Source ecological literature:
Grove, S.J. (2009b). Beetles and fuelwood harvesting: a retrospective study from Tasmania’s southern forests. Tasforests 18: 77-99.
Baker, S.C. (2006b). Ecology and conservation of ground-dwelling beetles in managed wet eucalypt forest: edge and riparian effects. PhD thesis, Univ. of Tasmania, Hobart.
Grove, S. et al. (2009). A long-term experimental study of saproxylic beetle … succession in Tasmanian Eucalyptus … logs… In: Fattorini, S. (Ed.), Insect Ecology and Conservation. Research Signpost, pp. 71-114.
Grove, S.J. & Yaxley, B. (2005). Wildlife habitat strips and native forest ground-active beetle assemblages in plantation nodes in northeast Tasmania. Aust. J. Entom. 44 (4): 331-343.
Grove, S.J. (2009c). Do wildlife habitat strips act as refuges for mature-forest carabid beetle assemblages? A case-study in Tasmanian wet eucalypt forest, Australia. For. Ecol. Manage. 259: 496-504.
Harrison, K.S. (2007). Saproxylic beetles associated with habitat features in Eucalyptus obliqua trees in the southern forests of Tasmania. PhD thesis, Dept. of Zoology, Univ. of Tasmania, Hobart.
Michaels, K.F. (1999a). Carabid beetles as biodiversity and ecological indicators. PhD thesis, Univ. of Tasmania, Hobart.
Michaels, K.F. (1999b). Carabid … communities in Tasmania: classification for nature conservation. In: Ponder, W. & Lunney, D. (Ed.), The Other 99%: …. Roy. Zool. Soc. NSW, pp. 374-379.
Taylor, R.J. et al. (2000). Occurrence of old-growth carabid beetles in retained unlogged strips in … southern Tasmania. In: Saunders, D. et al. . (Eds.), Nature Conservation 5…. Surrey Beatty, pp. 120-127.
Yee, M. (2005). The ecology and habitat requirements of saproxylic beetles native to Tasmanian wet eucalypt forests: potential impacts of commercial forestry practices. PhD thesis, Univ. of Tasmania, Hobart.
Yee, M. et al. (2006). Brown rot in inner heartwood: why large logs support characteristic … beetle assemblages … In Grove, S.J. & Hanula, J.L. (eds.) Insect biodiv. and dead wood, pages 42-56. USDA For. Serv., SRS.