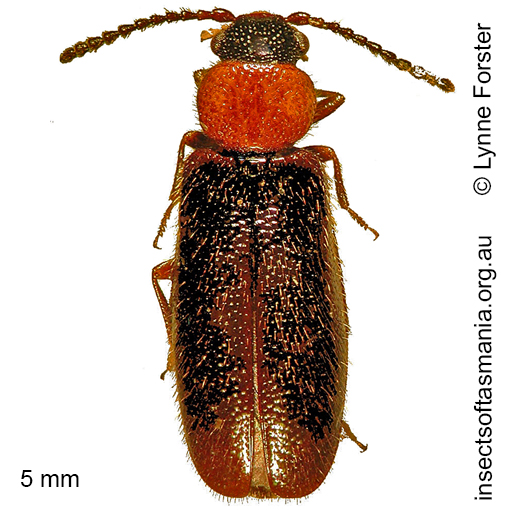
Temnopalpus bicolor Blackburn, 1888 (a species of fire-coloured beetle)
Basis for Tasmanian occurrence
Semmens, T.D., McQuillan, P.B. & Hayhurst, G. (1992). Catalogue of the Insects of Tasmania. Government of Tasmania: Department of Primary Industry, 104 pp. (as Temnopalpus tricolor)
TMAG collections
Classification
Order: Coleoptera
Suborder: Polyphaga
Superfamily: Tenebrionoidea
Family: Pyrochroidae
Subfamily: Pilipalpinae
Morphology
Typical length (mm): 5
Flightedness: winged and assumed capable of flight
Source literature on morphology and taxonomy (*primary taxonomic source, where identified):
*Blackburn, T. (1888). Further notes on Australian Coleoptera, with descriptions of new species. Trans. Proc. Roy. Soc. S.A. 10: 177-287.
Ecology
Assumed larval feeding: wood-feeder
Association with dead wood or old trees: obligately saproxylic
Ecological attributes: — May occupy logs or trunks of Eucalyptus obliqua, at least temporarily, since found having emerged within six years of felling (Grove et al., 2009).
Collection method(s) for TMAG material: — Emergence trapping from log of Eucalyptus obliqua — Knockdown fogging of canopy of Nothofagus cunninghamii — Malaise trapping — Sticky trapping on Eucalyptus obliqua — Trapping using a range of devices placed in crown of Eucalyptus obliqua (Bar-Ness, 2005).
Source ecological literature:
Bar-Ness, Y. (2005). Crown structure and the canopy arthropod biodiversity of 100 year old and old-growth Tasmanian Eucalyptus obliqua. Msc thesis, Univ. of Tasmania, Hobart.
Grove, S. et al. (2009). A long-term experimental study of saproxylic beetle … succession in Tasmanian Eucalyptus … logs… In: Fattorini, S. (Ed.), Insect Ecology and Conservation. Research Signpost, pp. 71-114.
Harrison, K.S. (2007). Saproxylic beetles associated with habitat features in Eucalyptus obliqua trees in the southern forests of Tasmania. PhD thesis, Dept. of Zoology, Univ. of Tasmania, Hobart.
Yee, M. (2005). The ecology and habitat requirements of saproxylic beetles native to Tasmanian wet eucalypt forests: potential impacts of commercial forestry practices. PhD thesis, Univ. of Tasmania, Hobart.