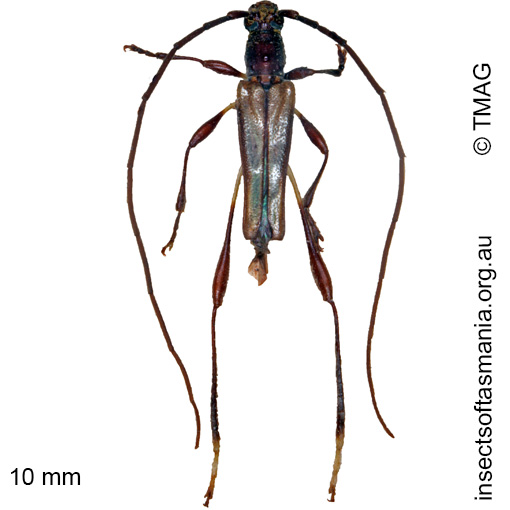
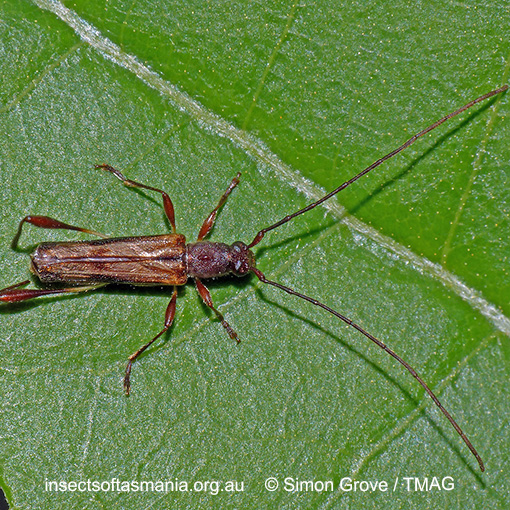
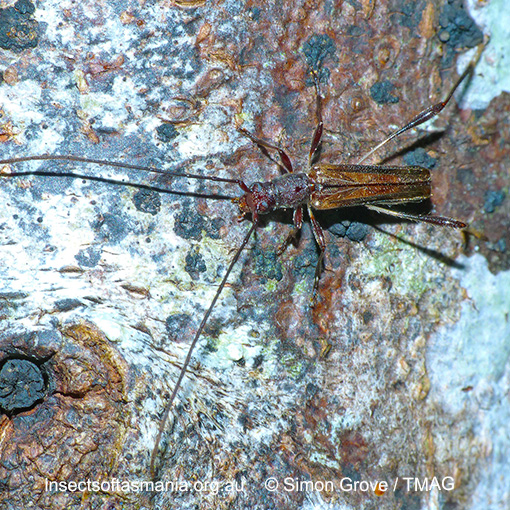
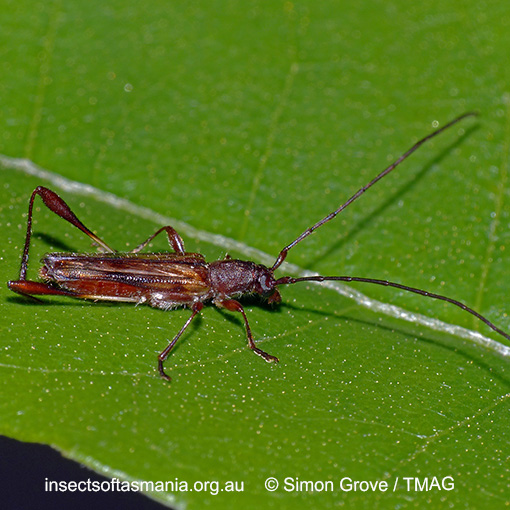
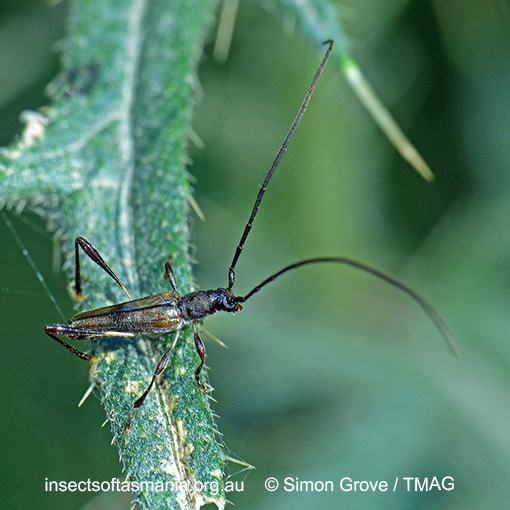
Mecynopus cothurnatus
Basis for Tasmanian occurrence
TMAG collections
Classification
Suborder: Polyphaga
Superfamily: Chrysomeloidea
Family: Cerambycidae
Subfamily: Cerambycinae
Tribe: Molorchini
Morphology
Flightedness: winged and assumed capable of flight
Source literature on morphology and taxonomy (*primary taxonomic source, where identified):
*Erichson, W.F. (1842). Beitrag zur Insecten-Fauna von Vandiemensland, mit besonderer Beruecksichtung der geographischen Verbreitung der Insecten. Nicolai’schen Buchhandlung 8(1): 379 pages.
Ślipiński, A. & Escalona, H. (2016). Australian longhorn beetles (Coleoptea: Cerambycidae), Volume 2: Subfamily Cerambycinae. CSIRO publishing, 640 pp.
Ecology
Association with dead wood or old trees: obligately saproxylic
Ecological attributes: — Acacia dealbata is a host-plant (Bashford, 1990a) — Acacia mearnsii is a host-plant (Bashford, 1990a) — Acacia verniciflua is a host-plant (Bashford, 1990a) — Pinus radiata is a host-plant (Bashford, 1990a) — Breeds in dead or dying Acacia dealbata trees (Bashford, 1991) — May occupy logs or trunks of Eucalyptus obliqua, at least temporarily, since found having emerged within six years of felling (Grove et al., 2009).
Collection method(s) for TMAG material: — At light (with use of light-trap) — Baited trapping (funnel trap) — Beating vegetation (species not specified) — Emergence trapping from log of Eucalyptus obliqua — Hand collection (substrate not specified) — Hand collection from within log (tree species not specified) — Malaise trapping — Not specified — Rearing in insectary (host not documented) — Rearing in insectary from Acacia dealbata — Rearing in insectary from Acacia mearnsii — Rearing in insectary from Cassinia aculeata — Rearing in insectary from Juglans regia — Sticky trapping on Eucalyptus obliqua — Trapping using a range of devices placed in crown of Eucalyptus obliqua (Bar-Ness, 2005) — Trunk window trapping (Harrison, 2007).
Source ecological literature:
Grove, S.J. (2009b). Beetles and fuelwood harvesting: a retrospective study from Tasmania’s southern forests. Tasforests 18: 77-99.
Bar-Ness, Y. (2005). Crown structure and the canopy arthropod biodiversity of 100 year old and old-growth Tasmanian Eucalyptus obliqua. Msc thesis, Univ. of Tasmania, Hobart.
Bashford, R. (1990a). Tasmanian forest insects and their host plants: records from the Tasmanian Forestry Commission insect collection. Hobart: Tas. Forestry Commission, 32 pages.
Bashford, R. (1991). Wood-boring Coleoptera and associated insects reared from Acacia dealbata Link in Tasmania. Aust. Entom. Mag. 18 (3): 103-110.
Grove, S. et al. (2009). A long-term experimental study of saproxylic beetle … succession in Tasmanian Eucalyptus … logs… In: Fattorini, S. (Ed.), Insect Ecology and Conservation. Research Signpost, pp. 71-114.
Harrison, K.S. (2007). Saproxylic beetles associated with habitat features in Eucalyptus obliqua trees in the southern forests of Tasmania. PhD thesis, Dept. of Zoology, Univ. of Tasmania, Hobart.
Yee, M. (2005). The ecology and habitat requirements of saproxylic beetles native to Tasmanian wet eucalypt forests: potential impacts of commercial forestry practices. PhD thesis, Univ. of Tasmania, Hobart.