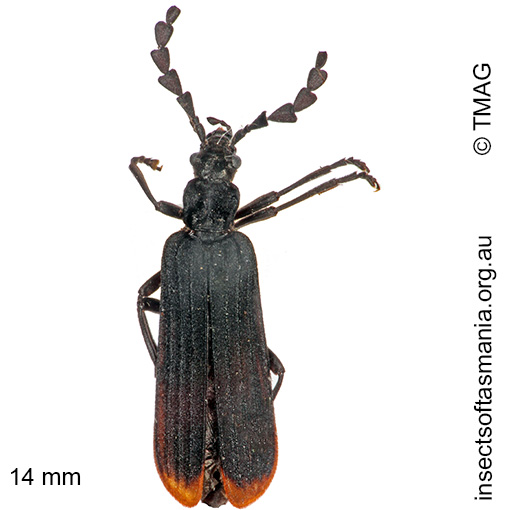
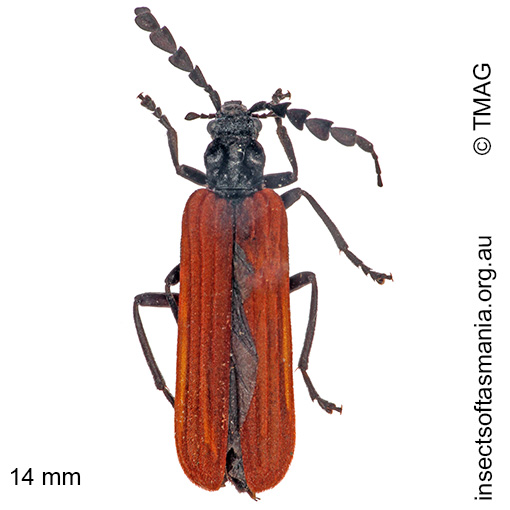
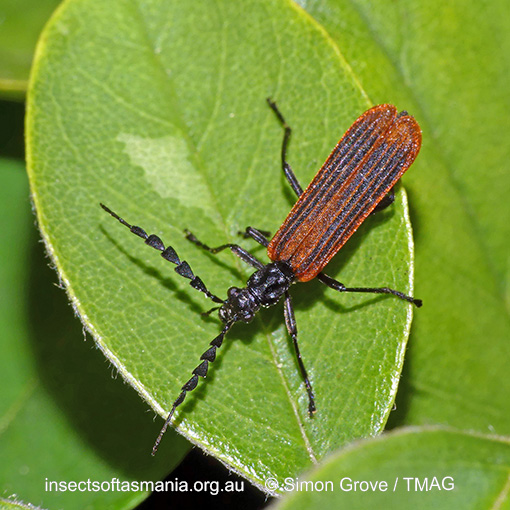
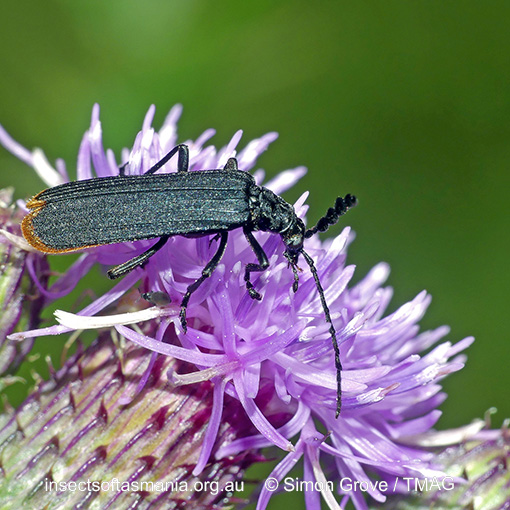
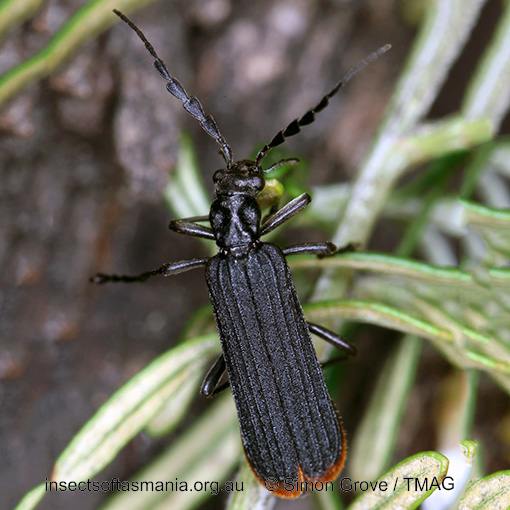
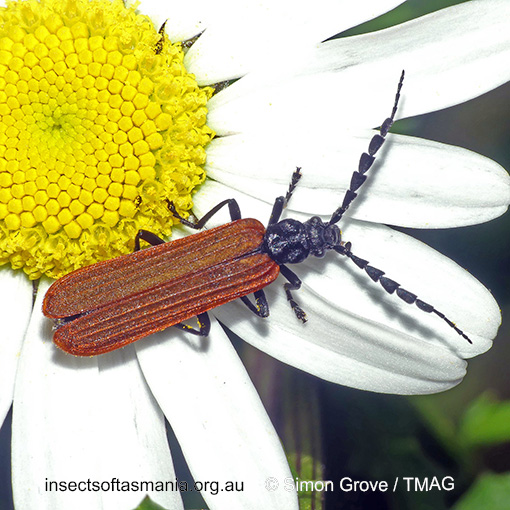
Pseudolycus haemorrhoidalis (a species of false blister-beetle)
Basis for Tasmanian occurrence
Semmens, T.D., McQuillan, P.B. & Hayhurst, G. (1992). Catalogue of the Insects of Tasmania. Government of Tasmania: Department of Primary Industry, 104 pp. (as Pseudolycus cinctus; Pseudolycus haemorrhoidalis)
TMAG collections
Classification
Order: Coleoptera
Suborder: Polyphaga
Superfamily: Tenebrionoidea
Family: Oedemeridae
Subfamily: Oedemerinae
Tribe: Asclerini
Morphology
Typical length (mm): 14
Flightedness: winged and assumed capable of flight
Source literature on morphology and taxonomy (*primary taxonomic source, where identified):
*Fabricius, J.C. (1801). Systema Eleutheratorum secundum ordines, genera, species: adiectis synonymis, locis, observationibus, descriptionibus. 2. Bibl. Acad. Nov., Kill., 610 pages.
Ecology
Assumed larval feeding: wood-feeder
Association with dead wood or old trees: obligately saproxylic
Ecological attributes: — May occupy logs or trunks of Eucalyptus obliqua, at least temporarily, since found having emerged within a year of felling (Grove & Bashford, 2003) — May occupy logs or trunks of Eucalyptus obliqua, at least temporarily, since found having emerged within six years of felling (Grove et al., 2009).
Collection method(s) for TMAG material: — Baited trapping (funnel trap) — Emergence trapping from log of Eucalyptus obliqua — Hand collection (substrate not specified) — Hand collection from flowers of Eucryphia lucida (Ettershanks & Ettershanks, 1993) — Hand collection from flowers of Helichrysum purpurascens (Ettershanks & Ettershanks, 1993) — Hand collection from flowers of Leptospermum sp. (Ettershanks & Ettershanks, 1993) — Malaise trapping — Not specified — Pipe trapping — Pitfall trapping — Sticky trapping on Eucalyptus obliqua.
Source ecological literature:
Grove, S.J. & Bashford, R. (2003). Beetle assemblages from the Warra log decay project: insights from the first year of sampling. Tasforests 14: 117-129.
Baker, S.C. (2006b). Ecology and conservation of ground-dwelling beetles in managed wet eucalypt forest: edge and riparian effects. PhD thesis, Univ. of Tasmania, Hobart.
Grove, S. et al. (2009). A long-term experimental study of saproxylic beetle … succession in Tasmanian Eucalyptus … logs… In: Fattorini, S. (Ed.), Insect Ecology and Conservation. Research Signpost, pp. 71-114.
Harrison, K.S. (2007). Saproxylic beetles associated with habitat features in Eucalyptus obliqua trees in the southern forests of Tasmania. PhD thesis, Dept. of Zoology, Univ. of Tasmania, Hobart.
Yee, M. (2005). The ecology and habitat requirements of saproxylic beetles native to Tasmanian wet eucalypt forests: potential impacts of commercial forestry practices. PhD thesis, Univ. of Tasmania, Hobart.